Huang He
"Yellow River-China's sorrow" that stretches nearly 3,000 miles across Northern China flowing west to east
Chang Jiang
Yangzi River that cuts through central China-longest river in Asia, flows from Tibet mountains to Pacific Ocean
Xia Dynasty
legendary dynasty founded by Yu the Great around 2200 BC
Yu the Great
legendary founder of the Xia Dynasty who was said to dig channels to drain the water to the ocean, creating the rivers of China
Shang Dynasty
(1500BC-1050BC) The first dynasty with clear evidence established in the Huang He Valley, northern China and developed China's first writing system.
Zhou Dynasty
(1050BC-400BC) Longest dynasty in Chinese history. Established a new political order with king at the highest level, then lords and warriors and then peasants.
lords
People of high rank
peasants
Farmers with small farms
Confucius
(551BC-479BC) Most influential teacher in Chinese history who believed in the return to ethics to restore family order and social harmony.
The Analects
The followers of Confucius compiled his sayings in this book.
Mandate of Heaven
Heaven gave power to the king, and no one ruled without heaven's permission. If a king was found to be bad, heaven would support another leader.
Confuciansm
Philosophical and religious teachings of Confucius: people should be respectful/loyal to their family members, leaders should be kind and lead by example, learning is a never ending process, heaven expects people to behave well and act morally.
Daoism
Stressed living in harmony with the Dao ("the way") the guiding force of all reality. They believed that people should be like water and simply let things flow in a natural way. Universe is a balance of opposites (female and male) and should be in harmony.
Laozi
(500sBC or 400sBC) The most famous Daoist teacher that taught that people should not try to gain wealth or power.
The Way and Its Power
Laozi's basic text of Daoism.
Legalism
(Political philosophy) The belief that people were bad by nature and needed to be controlled by strict laws and punishments. Unity and efficiency were important and the preparation of war to expand the empire.
Qin Dynasty
(221BC-206BC) Dynasty that united the country under one government and a system of standardization.
Terra-cotta soldiers
Discovered in 1974 in Xian in the tomb of Shi Huangdi was 6000 life size clay soldiers that were guardians of his tomb in the afterlife.
The Great Wall
Barrier that linked earlier walls across China's northern frontier. First section had been built in the 600sBC, Shi Huangdi connecting earlier pieces to form a long, unbroken structure to stop invaders from the north.
Han Dynasty
(206BC-AD220) Dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. Family life was supported and strengthened and this Dynasty made many achievements in art, literature, and learning.
Liu Bang
A peasant that led the army and because of the "mandate of heaven" became the first emperor of the Han Dynasty. He lowered taxes and relied on educated officials to help him rule.
Emperor Wudi
140BC became Emperor of Han Dynasty and created a strong central government by taking land from the lords and raising taxes. Confuciansm became China's government philosophy.
sundial
Han invention that uses the position of shadows cast by the sun to tell the time of day.
seismograph
Han invention that is a device that measures the strength of an earthquake.
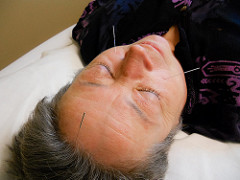
acupuncture
Han innovation that improved medicine and is the practice of inserting fine needles through the skin at specific points to cure disease or relieve pain.
silk
A soft, light, highly valued fabric made from the cocoons of the "----worm".
Silk Road
4,000 mile long network of routes that stretched westward from China across Asia's deserts and mountain ranges, through the Middle East until it reached the Mediterranean Sea. Named after the most famous item transported.
diffusion
The spread of ideas from one culture to another.
Example: Buddhism spread from India to China along the Silk Road. It offered re-birth and relief from suffering.
Warring States
(481BC-221BC) Civil war period that occurred at the decline of Zhou period until Qin Dynasty Shi Huangdi unified China.
Gobi Desert
One of the physical barriers that separates China from its northern neighbors.
oracle bones
questions written on bones and shells were heated, and priests read the cracks predicting the future