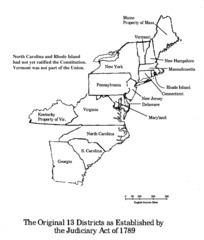
Judiciary Act of 1789
law that set up the federal court system
Alexander Hamilton
An early Federalist leader and first secretary of the treasury. He was killed in a duel with the Vice-president.
cabinet
leaders of the executive departments and others who serve as the advisers to the president
Bank of the United States
a national bank funded by the federal government and wealthy investors
(Democratic) Republicans -
Thomas Jefferson's political party - came from the Anti-federalists
two-party system
political system in which two parties compete on a mostly even basis for power
protective tariff
a tax on imported goods to protect domestic businesses
excise tax
a tax on specific goods produced within the country - like whiskey for example
neutrality
A position of not taking sides in a conflict
Thomas Pinckney
U.S. ambassador who asked Spanish officials to reopen New Orleans to U.S. trade.
John Jay
1st Chief Justice of the Supreme Court and early federalist leader, he negotiated with British for George Washington.
sectionalism
A devotion to the interests of one geographic region over the interests of the country as a whole
XYZ affair
A 1797 incident in which French officials demanded a bribe from U.S. diplomats
Alien and Sedition Acts
(1798) laws passed by a Federalist-dominated Congress aimed at protecting the government from treasonous ideas, actions, and people
nullification
A state's refusal to recognize an act of Congress that it considers unconstitutional
Aaron Burr
He almost won the election of 1800 but became Jefferson's Vice President; killed Alexander Hamilton in a duel
John Marshall
1755-1835. U.S. Chief Supreme Court Justice. Oversaw over 1000 decisions, including Marbury v Madison and McCulloch v. Maryland.
Judiciary Act of 1801
a law that increased the number of federal judges, allowing President John Adams to fill most of the new posts with Federalists
midnight judges
The 16 judges that were added by the Judiciary Act of 1801 that were called this because Adams signed their appointments late on the last day of his administration.
Marbury vs. Madison
This case establishes the Supreme Court's power of Judicial Review
judicial review
A power given to the judiciary branch in order to sustain checks and balances. This power let judges examine a law or act passed by the government to see if it was constitutional or not.
Louisiana Purchase
Large territory in western United States purchased from France in 1803 for $15 million. Doubled size of the country.
Lewis and Clark
Leaders of an expedition sent by Jefferson to gather information on the United States' new land and map a route to the Pacific. They kept very careful maps and records of this new land acquired from the Louisiana Purchase.
Sacajawea
native american woman who served as a guide an interpreter for the Lewis and Clark expedition
blockade
An act of sealing off a place to prevent goods or people from entering or leaving by way of the sea
impressment
British practice of taking American sailors and forcing them into military service
embargo
A government order imposing a trade barrier
Tecumseh
A Shawnee chief who worked to unite the Northwestern Indian tribes and was killed fighting for the British during the War of 1812 at the Battle of the Thames in 1813.
war hawk
Someone favoring war in a debate over whether to go to war, or whether to continue or escalate an existing war
Andrew Jackson
Leader of American forces at the Battle of New Orleans and 7th president of the U.S.
Treaty of Ghent
1814 treaty that ended the war of 1812
armistice
a temporary peace, halt in fighting