Muhammad Shah II
Turkic ruler of Muslim Khwarazm kingdom; attempted to resist Mongol conquest; conquered in 1220.
Khwarazm
An old Islamic empire that was invaded by the Mongols under Chingiss Khan. Modern day country of Uzbekistan
Barbarian
(n) : a person in a savage, primitive state; uncivilized person.
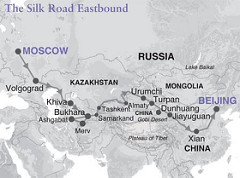
Silk Road
An ancient trade route between China and the Mediterranean Sea extending some 6,440 km (4,000 mi) and linking China with the Roman Empire. Marco Polo followed the route on his journey to Cathay.
Samarkand
an oasis town along the silk roads in central Asia; place where merchants & caravans found food, rest, lodging, and markets; became cosmopolitan center; conquered by the Mongols; During the rule of Timur Lane was the most influential captial city, a wealthy trading center known for decorated mosques and tombs.
Karakorum
Capital of the Mongol empire under Chinggis Khan, 1162 - 1227.
Temujin
name of Chinggis Khan when he was a youth; father was poisoned, and he was thrust into a leadership position; camp was raided and he was taken prisoner; escaped, joined a powerful clan; within a decade he had defeated all of his rivals and gained the name Chinggis Khan
Kuriltai
Meeting of all Mongol chieftains at which the supreme ruler of all tribes was selected
Khagan
Title of the supreme ruler of the Mongol tribes.
Khan
Title given to Mongol leaders, meaning "supreme ruler"
Cavalry
units of troops on horseback
Tumens
Basic fighting units of the Mongol forces; consisted of 10,000 cavalrymen; each unit was further divided into units of 1000, 100 and 10.
Xi Xia
Kingdom of the Tangut people, north of Song Kingdom, in the mid-11th century; collected tribute that drained Song resources and burdened chinese peasantry.
Jin Empire
Established by the Jurchen people in Northern China after they conquered the northern part of the Song Dynasty; Ruled from 1115-1234; Attacked by Chinggis and the Mongols in 1211
Kara Khitai
Empire established by Mongolians speaking peoples from 907-1118; conquered by Chinggis in 1219
Shamanistic
the animistic religion in which mediation between the visible and spirit worlds are effected by shamans (religious leaders)
Animism
the belief that spirits living in animals, plants and natural forces play an important role in daily life.
Batu
ruler of the golden horde; one of Chinggis Khan's grandsons; responsible for the invasion of Russia beginning in 1236.
Alexander Nevskii
Prince of Novgorod (r. 1236-1263). He submitted to the invading Mongols in 1240 and received recognition as the leader of the Russian princes under the Golden Horde.
Romance of the West Chamber
Chinese novel written during the Yuan Period; indicative of the continued literary vitality of China during Mongol rule.
Chinggis Khan
Born in 1170s in decades following death of Kabul Khan; elected khagan of all Mongol tribes in 1206; responsible for conquest of northern kingdoms of China, territories as far west as the Abbasid regions; died in 1227, prior to conquest of most of Islamic world.
Jochi
Eldest son of Genghis Khan and Borte. legitimacy was always questioned because of his conception time.
Ogedei
Third son of Chinggis Khan; succeeded Chinggis Khan as khagan of the Mongols following his father's death
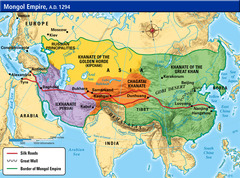
Golden Horde
Mongol khanate founded by Genghis Khan's grandson Batu. It was based in southern Russia and quickly adopted both the Turkic language and Islam. Also known as the Kipchak Horde.
Khanates
The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
Battle of Kulikova
Russian army victory over the forces of the Golden Horde; helped break Mongol hold over Russia
Prester John
In legends popular from the 12th to 17th centuries, he was a mythical Christian monarch whose kingdom was cut off from Europe by Muslim conquests; Chinggis Khan was originally believed to be this ruler.
Hulegu
(1217 - 1265) Ruler of the Ilkhan khanate; grandson of Chinggis Khan; responsible for capture and destruction of Baghdad in 1257.
Berke
(1257-1266) A ruler of the Golden Horde; converted to Islam; his threat to Hulegu combined with the growing power of Mamluks in Egypt forestalled further Mongol conquest in the Middle East.
Mamluks
Muslim slave warriors; established a dynasty in Egypt; defeated the Mongols at Ain Jalut in 1260 and halted Mongol advance
Baibar
Mamluk commander who defeated the Mongol army in the Middle East
Kubilai Khan
Grandson of Chinggis Khan; commander of Mongol forces responsible for conquest of China; became khagan in 1260; established Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1271.
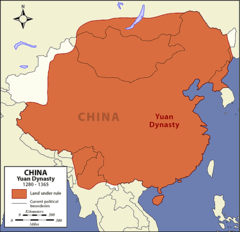
Yuan
the imperial dynasty of China (1279-1368) established by Kubilai Khan; During this dynasty, the Silk Road became safer for travelers because it was monitered by patrols.
Tatu
Mongol capital of Yuan dynasty; present-day Beijing
Chabi
Influential wife of Kubilai Khan; promoted interests of Buddhists in China; indicative of refusal of Mongol women to adopt restrictive social conventions of Chinese.
White Lotus Society
Secret religious society dedicated to overthrow of Yuan dynasty in China; typical of peasant resistance to Mongol rule
Ju Yuanzhang
Chinese peasant who led successful revolt against Yuan; founded Ming dynasty
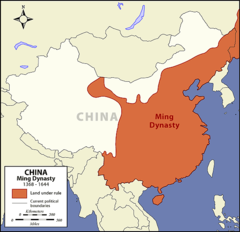
Ming Dynasty
Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China.
Tamerlane
Also known as Timur; leader of Turkic nomads; beginning in 1360s from base at Samarkand launched series of attacks in Perisan, the Fertile Crescent, India and southern Russia; empire disintegrated after his death in 1405
Best Global Teacher
I love Mrs. Crotty