Middle Ages
The era in European history that followed the fall of the Roman Empire, lasting from about 500 to 1500 - also called the medieval period. This period of time in Europe combines the classical heritage of Rome, the beliefs of the Roman Catholic Church, and the customs of Germanic tribes.
Franks
The Germanic people who lived and held power in Gaul. Their leader was Clovis and he would later bring Christianity to the region. By 511 the Franks had united into one kingdom and they controlled the largest and strongest parts of Europe.
Monastery
A place where communities of monks live lives of devotion to God in isolation from the outside world.
Secular
Things concerned with worldly matters rather than spiritual, or church matters.
Carolingian Dynasty
The family that ruled the Franks from 751 to 987. The Dynasty was started by Pepin The Short, and brought to the hight of its power by his son Charlemagne.
Charlemagne
The Frankish king who conquered most of Europe and was crowned Holy Roman Emperor by Pope Leo III in the year 800.
Lord
In the feudal system this person was a landowner, who could grant fiefs (land) to a vassal.
Fief
Land granted by a lord to a vassal in exchange for loyalty and service.
Vassal
A person granted land from a lord in return for loyalty and service.
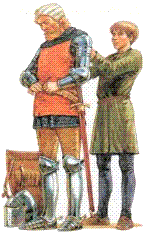
Knight
A man who received honor and land in exchange for serving a lord as a soldier. These were well trained soldiers who fought on horseback for their chosen lord.
Serf
A peasant laborer who was bound by law to the lands of a noble. He was different from a slave in that he could not be bought or sold but in everyother way was owned by his feudal lord.
Manor
A large estate, often including farms and a village, ruled by a lord.
Tithe
Also known as a Church tax, this was a tenth of a family's income given to the church.
Chivalry
This was a Code of conduct for knights during the Middle Ages in which they were required to be loyal to their feudal lord, God, and their chosen lady.
Tournament
Mock battle in which knights would compete against one another to show off their fighting skills.
Troubadour
A medieval poet and musician who traveled from place to place, entertaining people.
Clergy
Religious officials, such as priests, given authority to conduct religious services.
Sacrament
These are important religious ceremonies, in the Christian church, that help pave the way to salvation. [ex. Baptism, Communion, Marriage]
Canon Law
The body of laws governing the religious practices of the Christian church and its members.
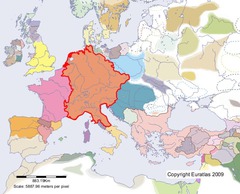
Holy Roman Empire
A political entity in Europe that began with the papal coronation of Otto I as the first emperor in 962. It was a weak political association of independent states in Germany and Italy.
Lay Investiture
The appointment of religious officials by kings or nobles.
Charles Martel
Also known as Charles the Hammer. The Carolingian monarch of the Franks who was responsible for defeating Muslims at the battle of Tours in 732, which ended the Muslim threat to western Europe.
Charles the Bald
He was the grandson of Charlemagne who received the western part of the empire (modern day France) after it was divided between the 3 brothers of Louis the Pious.
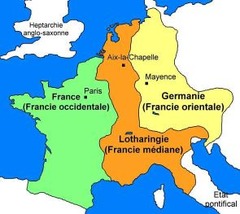
Lothair
He was the eldest son of Louis the Pious, who took the middle kingdom and the title of Emperor after the kingdom was split between the 3 brothers.
Louis the German
He was a son of Louis the Pious, who took control of the area of modern day Germany when the empire was divided between he and his brothers.
Treaty of Verdun
The treaty that divided the carolingian empire into three sections, to be split between the three sons of Louis the Pious, signed in 843.
Leif Ericson
The Viking explorer believed to be the first European to reach the New World (in about 1000 AD).
Eleanor of Aquitaine
A powerful French duchess she divorced the king of France and then married Henry II of England. Together they ruled all of England and about 1/2 of France. She was the mother of King Richard the Lion-Hearted, and King John.
Richard the Lion-Hearted
The King of England from 1189 to 1199, he was the son of King Henry II and Queen Eleanor of Aquitaine. He fought in the Holy Land against Saladin during the Third Crusaded eventually ending in a truce.
Otto the Great
He was made king of Germany in 936 and formed a close alliance with the Church in order to limit the power of the nobles. In return for his military service to the pope he was crowned Holy Roman Emperor in 962, creating the Holy Roman Empire.
Fredrick I "Barbarossa"
Called Barbarossa because of his red beard he was known as a powerful personality and military. He was the German king who ruled the Holy Roman Empire, being the first one to call it that, until his death in 1190.
Battle of Legnano
This battle took place in 1176 between Fredrick I "Barbarossa", and the Lombard League (a group of Italian merchants) who were joined by the Pope. Fredrick's knights were beaten by the Lomard League's foot soldiers who were using cross bows, forcing him to ask for peace.
Einhard
A medival monk and secretary of Charlemagne who wrote his biography.
Benedict
An Italian monk who lived from 480-547 and founded the Benedictine order. He wrote a set of rules to be followed in order to live a holy life.
Scholastica
She was the sister of Benedict who headed a convent and adapted her brothers rules, for a holy life, for women.
Venerable Bede
He was an English monk who wrote a history of England in 731, which is considered one of the best works of the midieval ages.
Gregory I
He was a strong pope, known as Gregory the Great, who strengthened the power of the papacy (office of the pope) and the church. He extended his power to include worldly politics and not just spiritual matters.
Clovis
He was the Frankish king who converted the Franks to Christianity around 496. He was able to unite all the Frankish people into one kingdom under his rule by 511.
Louis the Pious
He was Charlemagne's only surviving son who ruled the Carolingian empire from 814-840. He was a very devout man but an inept leader who divided the empire between his 3 sons brining an end to Carolingian empire.
Northmen
Another name for Vikings these were Germanic people who attacked and pillaged the people of Europe.
Vikings
Also known as "Norsemen" or "Northmen" these German and Scandinavian peoples raided Europe from the 700's through the 1100's.
Magyars
This nomadic group attacked Western Europe from the east, sweeping across the plains of the Danube River. They came from what is now Hungary and were known for their great horsemanship.
Lombards
A Germanic people who invaded northern Italy in the 6th century and later parts of western Gaul(France). When they attacked Rome they were defeated by Charlemagne who was then crowned Emperor as thanks for his service.
Abbots
These men were the religious leaders of a monastery.
Emperor Henry IV
He fought against Pope Gregory VII over the power to choose church officials and was excommunicated. He had to beg for forgiveness for three days in the cold in order to be let back in the church.
Pope Leo III
He crowned Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor on Christmas Day, 800.
The Song of Roland
A famous medieval epic poem that praises a band of French soldiers who perished in battle during Charlemagne's reign.
Excommunication
This was a form of punishment for not following Church law. It ment that a person was banned from the Church and its sacraments, in other words, you could not go to heaven.
Interdict
The pope could forbid priests to give the sacraments of the Church to the people of a town, or a country (kicking them out of the church). This was a weapon of the Roman Catholic church in order to punish those who went against the Pope.
Pope Gregory VII
He banned Lay Investitures because he thought popes should have the power to name bishops not the kings. He excommunicated Henry IV because he spoke out against him over this issure causing a standoff that Gregory eventually won.
Concordat of Worms
A compromise between the king and the Pope that stated that the church alone could grant a church position, but the King would have the right to veto the possition.
Page
A young boy, usually around the age of 7, who was sent to a castle to learn courtly manners and begin his training to become a knight.
Squire
When a Page reached the age of 14 he was able to become a servant of a Knight who would then train him.
Caltrops
Two inch iron spikes thrown on battlefields intended to wound horses.