Indo-Europeans
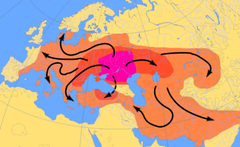
These people are thought to have been a nomadic tribe who came from the plains of the Caucasus Mountains, and then spread out from there.
Steppes
A dry grassland that is found north of the Caucasus Mountains, between the Black and Caspian Seas. The land is useful for raising herds and grazing flocks.
Migration
The movement of people or animals from one region to another.
Hittites
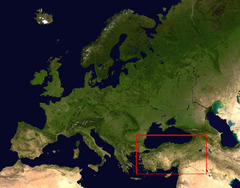
A Indo-European people group who lived in Anatolia, modern day Turkey, around 2000 B.C. They were skilled iron workers, and made advanced weapons that helped them forge an empire that would reach into Mesopotamia.
Anatolia
Also known as Asia Minor, or the country of Turkey, it is a large peninsula that juts out into the Mediterranean Sea. The land is mostly made up of high, rocky plateaus which provide an abundant supply of timber and minerals.
Aryans
A light skinned, tall, semi-nomadic group of herders who originated in the mountains between the Caspian and Aral seas. Around 1000 B.C. they invaded and conquered the Indus Valley creating their own kingdom.
Vedas
This is a collection of four, Aryan, religious texts which show prayers, magical spells, and instructions for performing rituals.
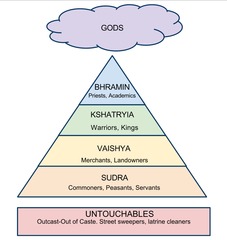
Brahmin
They were Aryan priests, and the most respected of the four main social groups of that culture.
Caste
This was a term coined by 15th c. Portuguese explorers to explain the social structure of the Indian people. The system was originally created by the Aryans to seperate their people from the groups they had conquered.
Mahabharata
One of the great epics of Indian literature which recounts the struggle of the Aryans to conquer India.
Reincarnation
The belief that a person's soul is reborn time and time again until that person discovers perfect knowledge known as Moksha.
Karma
A sort of record kept of all the good or bad things that a person has done in their life, which then affects them when they are reincarnated into their next life.
Jainism
A religion that was founded by Mahavira, in the 6th c. B.C., that believes that every living thing has a soul and thus should not be harmed.
Siddhartha Gautama
He was a young nobleman who after years of pampering decided to look for the meaning of life. He eventually became enlightened and from then on was know as Buddha, who founded the religion of Buddhism.
Enlightenment
To have great wisdom.
Nirvana
This is the highest level of enlightenment that a person can achieve in Buddhism. This is when a person is released from the human bondage of selfishness and pain.
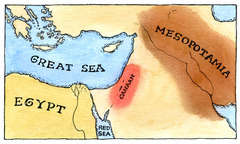
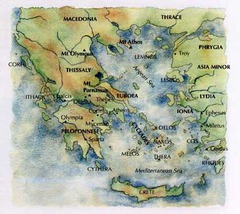
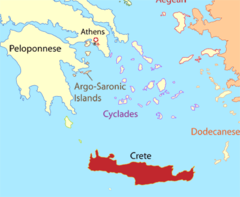
Minoans
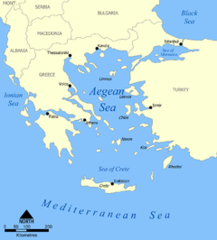
An ancient, seafaring culture that was centered around the island of Crete from 2000 to 4000 B.C. An extremely advanced and rich culture, they suddenly collapsed around 1200 B.C. when the Thera volcano violently erupted distroying their civilization.
Aegean Sea
The body of water that is found between Greece and the Anatolian Peninsula.
Knossos
This was the capital city of the Minoan people, located on the island of Crete. The city was first excavated in the late 19th, early 20th centuries, and showed that the Minoans were an advanced and largely peaceful people.
King Minos
He was the mythological king of Crete, who was said to have a monster called a Minotaur (half man, half bull), locked in a maze to kill his enemies.
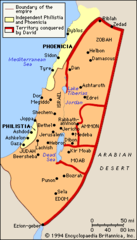
Phoenicians
These people did not have a united country, but instead occupied a number of city-states in the modern area of Lebanon. They were accomplished sailors, and ship builders, who became powerful traders in the Mediterranean region, around 1100 B.C.
Palestine
This was an area of land that would consist of modern day Isreal, Lebanon, Syria, and Jordan, that lie along the Mediterranean coast. This region would later be named Palestine by the Romans after the Philistine people who lived there.
Canaan
This was the ancient home of the Hebrew people, which included much of the area of Palestine.
Torah
These are the most sacred of the Hebrew writings, comprising the first 5 books of their bible. (What is also known as the Old Testament in the Christian faith.)
Abraham
He was a shepherd from the city of Ur, in Mesopotamia, who would later become known as the 'Father' of the Hebrew people. According to tradition he was commanded by God to move his family to the area of Canaan where he would start the Hebrew nation.
Monotheism
This is the belief in only one God.
Covenant
This is the agreement made between two people, or groups of people. In the Jewish (Hebrew) tradition, Abraham made a covenant with God that he and his descendents would worship no other gods.
Moses
The man who led the Hebrew people out of slaver, in Egypt, around 1300 B.C., or 1200 B.C. He was hidden by his mother in a basket, and placed on the river were he was discovered by Pharaohs daughter. Later after fleeing to the desert he was called on by God to lead the Hebrew people out of Egypt.
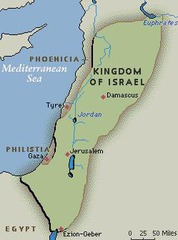
Israel
This was the land, along the Mediterranean Coast that was formaly called the land of Canaan. The Hebrew people conquered this land after they escaped Egypt, and formed the Kingdom of Israel.
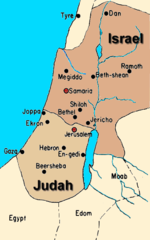
Judah
After the death of King Solomon the Kingdom of Israel broke into two separate kingdoms in 922 B.C. The Southern Kingdom was called Judah, after the tribe of Judah, from which the Hebrew people became known as 'Jews'.
Tribute
Money or goods paid to a powerful nation in order to ensure peace between you.
Untouchables
This is an Indian social group which exists outside of the Caste system. The people of this group are considered impure, and beneath animals in importance.
Upanishads
These are the interpretations of the Vedic Hymns, that Hindu teachers wrote down between 750 and 550 B.C.
Buddhism
A world religion or philosophy based on the teaching of the Buddha and holding that a state of enlightenment can be attained by suppressing worldly desire.
Moksha
This is the highest form of enlightenment that a person can achieve in Hinduism. A place of perfect being, which is achieved through the constant cycle of reincarnation.
Brahman
This is the world's soul, according to Hindu belief, and consists of the souls of everything on Earth. It is also believed that this great god of Hinduism, consists of three lesser gods; Vishnu, Shiva, and Brahma.
David
The second great king of Israel who came to power after the death of King Saul. He was a powerful, devout, and popular king who united all the tribes of Israel into one powerful kingdom, with Jerusalem as its capital. He is most famous for his battle with the Philistine giant Goliath, whom he killed with a sling-shot.
King Cyrus I
He was the great king of Persia who conquered the Babylonians in 539 B.C., allowed the Jewish people to return from exile, and gave the Jews help in rebuilding their temple.
Solomon
The greatest of all the Hebrew Kings, he was the son of King David and Bethsheba, ruling around 962 B.C. He was known for his wisdom and his many building projects in Jerusalem, including the new Temple.
Saul
Known as a great warrior, he was chosen the first King of the Hebrews. He became increasingly power hungery and jealous of others. After he was killed in battle his son-in-law David assended to the thrown.
Greeks
A Mediterranean people who were divided into warring city-states. Their culture was greatly influence by the Minoans, and Phoenician people.
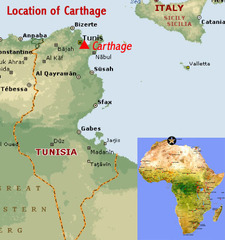
Carthage
This colony, founded by the Phoenicians in 814 B.C., was located in Nothern Africa, in what is now the country of Tunisia. This would be the greatest of all the Phoenician colonies.
Crete
Located on the edge of the Aegean Sea, this island served as the center of the Minoan Civilization.
Tyre
A popular trading port, this Phoenician city-state was known for its trade in a valuable purple dye.
Sangha
Traditionally these were Buddhist monks, but know it is a term used for anyone who follows Buddhism.
Dharma
In Hinduism, the divine law that rules karma; it requires all people to do their duty based on their status in society.
Asia Minor
This is the Peninsula, also known as Anatolia, which is surrounded on three sides by the Black Sea, Aegean Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Varnas
The strict social structure that the Aryans brought with them to the Indus Valley. It is derived from the word 'Varna', which means skin color, and eventually became known as the social structure.
Ten Commandments
This was the moral code that was given to Moses, by God, on top of Mount Sinai. These laws were the new covenant between the Hebrew people and God, which were supposed to tell the people how to live good lives.