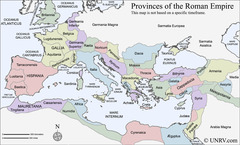
Republic
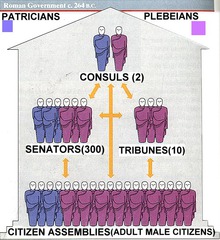
From the Latin prase meaning 'Public Affairs' this is a system of government in which officials are voted for by the people. This right was only given to free-born men, who were citizens of Rome.
Patrician
The hereditary aristocracy, or ruling class of ancient Rome who held most of the power. They believed they had the right to make the rules based on the fact that their power was handed down through the generations.
Plebeian
This group of ancient Romans made up most of the population, and consisted of farmers, artisans, and merchants.
Tribune
These were the officials elected by the plebeians to protect their rights from the unfair acts of the Patricians.
Consuls
Two officials from the patrician class who were appointed each year to lead the Roman Republic. They would supervise the government and command the armies during their terms of office. In case of disagreements one always had the right to veto (turn down) the others decision.
Senate
This 300 member branch of the Roman government controled both the legislative and administrative functions of the government. Originally only the aristocracy were allowed into the Senate but later the Plebians were allowed to join.
Dictator
This was a leader, who was elected by the Consuls, and approved by the Senate, to rule for six months during times of crisis. These men would have absolute power to make laws and control the military while in office.
Legion
This was the Roman military unit, made up of 5,000 foot soldiers (infantry). This unit could be further divided into smaller groups of 80 men, called a Century.
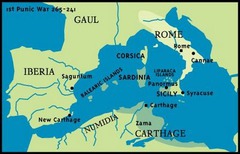
Punic Wars
A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage (264-146 B.C.); resulted in the destruction of Carthage and Rome's dominance over the western Mediterranean.
Hannibal
A brilliant, young, Carthaginian general who attacked Rome during the second Punic War. He famously marched an army of men and elephants across the Alps in an attempt to capture the city of Rome, and avenge the earlier defeat of Carthage. His attempt was unsuccessful and he was later defeated by the Romans at Zama in 202 B.C.
Civil War
A war between people in the same country.
Julius Caesar
A brilliant, Roman, military leader who conquered Gaul (modern day France) between 58 and 50 B.C. He then returned to Rome as a hero and was declared dictator for life in 44 B.C. That same year he was assassinated by a group of senators who were afraid Caesar might become a king.
Triumvirate
In ancient Rome, a group of three leaders sharing control of the government.
Augustus
The Latin term meaning "exalted one", was taken by Octavian, the adopted son of Julius Caesar, when he made himself emperor. This was the beginning of the Roman Empire.
Pax Romana
A period of peace and prosperity throughout the Roman Empire, lasting from 27 B.C. to A.D. 180.
Jesus
The Jewish teacher and prophet who was born in Judea, a province of the Roman Empire. He came as a religious leader and reformer, but was seen as a dangerious revolutionary by the Romans, and some Jewish leaders. He was arrested and crucified around 29 A.D., but is belived to have risen from the dead 3 days later. The followers of this man and his teachings are known today as Christians.
Apostle
Greek for "one sent forth" Refers to the twelve chosen by Jesus during his public ministry as his disciples.
Paul
He was a Follower, or Apostle, of Jesus who helped spread Christianity throughout the Roman world. He specifically ministered to the gentiles, or non-Jews.
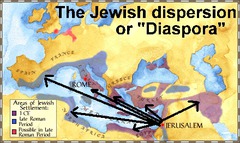
Diaspora
Meaning dispersal, The Romans forced the Jewish people out of Isreal after they attempted to win their freedom in 132 A.D., and scattered them throughout the Roman world.
Constantine
The Roman emperor who promoted tolerance to all religions in the roman empire and legalized Christianity in 313 A.D.
Bishop
A high-ranking priest, or Church official with authority over a local area, or diocese.
Peter
He was one of the 12 apostles of Jesus, and the first bishop of Rome. He is also believed by Roman Catholics to have been the first Pope.
Pope
The leader of the Roman Catholic church.
Inflation
The extreme drop in the value of money combined with the rise of prices.
Mercenary
A soldier who works for a foreign government in exchange for money.
Diocletian
The Emperor of Rome (284-305) who divided the empire into east and west (286) in an attempt to rule the territory more effectively. He ruled the empire with an iron fist and when he revived the old religion of Rome it led to the last major persecution of the Christians (303).
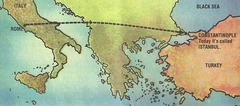
Constantinople
Previously known as Byzantium, Constantine changed the name of the city and moved the capitol of the Roman Empire here from Rome.
Attila
The Leader of the Huns who put pressure on the Rome's borders when he attacked the empire during the 5th c. A.D.
Greco-Roman Culture
Also known as Classical Civilization, this is the mixing together of Geek, Roman, and Hellenistic cultures.
Pompeii
The Roman city near Naples, Italy, which was buried during an eruption of Mount Vesuvius in A.D. 79. which preserved many buildings and art.
Virgil
Considered the greatest of the Roman poets, he wrote the epic poem the Aeniad. It tells of the hero Aeneas and praises Roman virtues.
Tacitus
A Roman historian who presented the facts accurately. He wrote about the good and the bad of imperial Rome in his Annals and Histories.
Aqueduct
Designed by Roman engineers these artificial channels brought water, over long distances, into cities and towns.
Etruscans
A people group, native to Italy, that ruled Rome for more than 100 years. Skilled metal workers they built up Rome and became a leading influence in the Roman culture.
Greeks
One of the original cultures of Rome, they migrated from across the Ionian Sea, from Greece, and settle in Southern Italy. They greatly influenced the culture of ancient Rome.
Tarquin the Proud
The last of the Roman kings who was known for his abusive rule. He was finally driven from the throne in 510 B.C., and led the Romans to declare they would never again be ruled by a king.
Latins
These ancient people were the first to settle in what would become the city of Rome, and are known as the first Romans.
Province
An area of the Roman Empire ruled by a governor, who was supported by an army.
Scipio
The great Roman general who commanded the invasion of Carthage in the second Punic War, and defeated Hannibal at Zama (circa 237-183 BC).
Cicero
He was a senator, and famous orator of Rome. Who was put to death for his veiws on the assassination of Caesar.
Octavian
He was Julius Caesar's succussor who later became known as Caesar Augustus. He was able to defeat Mark Antony to gain power over all of Rome and became Rome's first true emperor.
Mark Antony
The Roman general who was a close friend, and supporter of Julius Caesar. He was one of the three rulers who formed the Second Triumvirate along with Octavian and Lepidus. Later met Queen Cleopatra of Egypt and followed her to Egypt which led to warring between he and Octavian. He later committed suicide along with Cleopatra.
Cleopatra
The beautiful and charismatic queen of Egypt, who was a mistress of Julius Caesar, and later of Mark Antony. She killed herself to avoid capture by Octavian in 30 B.C.
Pompey
The Roman general, who along with Crassus, and Julius Caesar made up the first Triumvirate. He was an ally of Caesar but later the two went to war against eachother ending with Pompey's defeate, and murder in Egypt.
Absolute Ruler
A ruler who has unlimited power and controls all aspects of society.
Gladiators
Slaves in the Roman Empire, who were trained to fight to the death, for the entertainment of the Roman people.
Paterfamilias
Meaning 'Father of the Family', In Roman culture the eldest male relative had absolute power over his household.
Classical Civilization
Also known as Greco-Roman culture, this is a combination of Greek, Roman, and Hellenistic cultures. The ideas from all these cultures were incorporated into Roman art and literature.
Aeneid
The epic poem, writen by the Roman poet Virgil, that told the story of a great Trojan hero, Aeneas.
Annals and Histories
Written by Tacitus this book expressed the good and bad of imperial Rome.
Twelve Tables
The earliest written collection of Roman laws, drawn up by patricians at the request of the Plebians, about 450 B.C. These laws were carved on twelve tablets and became the foundation of Roman law.